Deploy an app
Deploy apps using the Edgeworx Portal UI or terminal commands via edgectl
Prerequisites
To deploy your custom app, you will need a
Edgeworx Cloud
account with at least one
node
accessible
and ONLINE. You will need a basic understanding
of
how to structure app YAML
for Edgeworx Cloud.
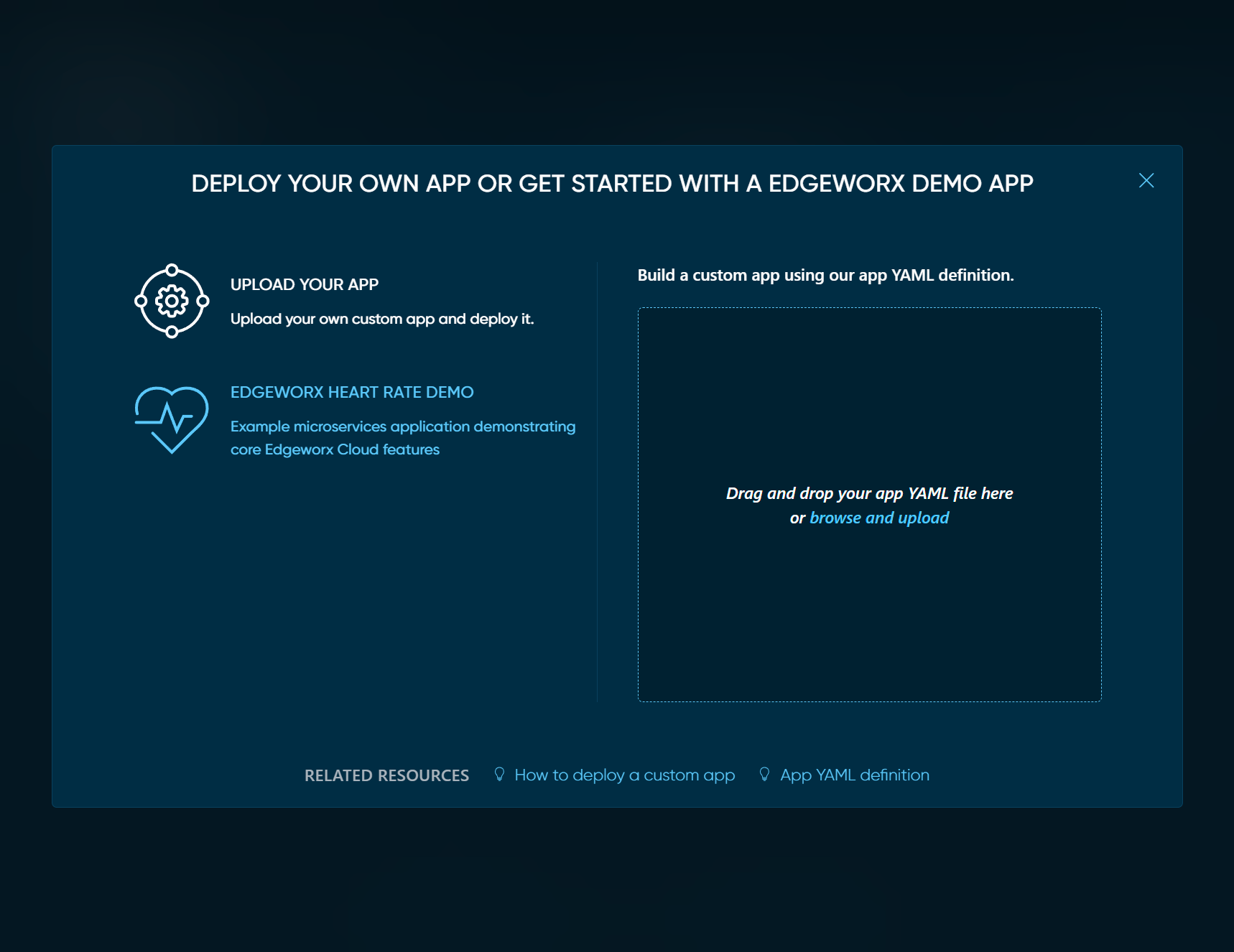
Deploy an App using Edgeworx Cloud Portal
- Go to the Edgeworx Cloud project page
- Select
Apps - Click on
+ DEPLOY APP - Drag n’ drop a YAML file into the box
View your Application Details
Click on your app in the list of applications to see its details.
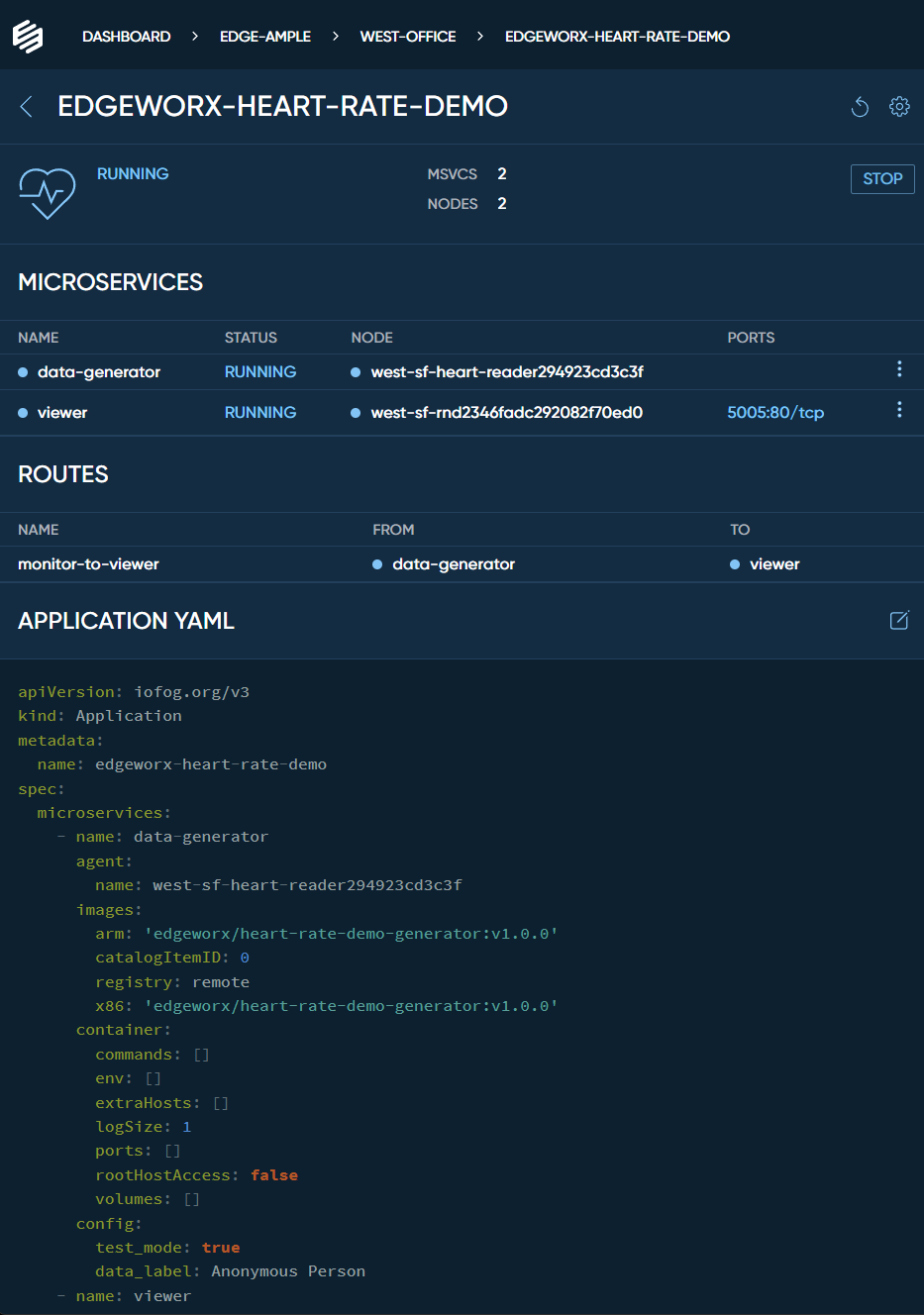
The app details page contains information about its microservices , routes, the nodes involved in running the microservices and its YAML Definition.
Edgeworx Cloud Portal allows you to edit your app YAML right in the browser. More information about the Application YAML files can be found here .
Deploy an App using edgectl
Once we have an edge node in our project, we can deploy applications to run on those nodes.
To deploy an app, use edgectl deploy app. We can run the following to learn how it works:
edgectl deploy app --help
The deploy app command requires a path to a YAML file to be specified. See the YAML
for our demo apps:
Heart Rate Demo
.
The YAML file defines everything about our edge application that is required to deploy it. For
example:
edgectl deploy app ./edgeworx-heart-rate.yaml
You can use edgectl commands to view details of the app.
$ edgectl get apps
NAME DESCRIPTION STATUS
edgeworx-heart-rate running
$ edgectl get app edgeworx-heart-rate
NAME DESCRIPTION STATUS
edgeworx-heart-rate running
If you need more detail on an app, use the --json flag,
e.g. edgectl get app edgeworx-heart-rate --json: (output abbreviated for clarity):
{
"description": "",
"id": 1,
"isActivated": true,
"name": "edgeworx-heart-rate",
"projectUUID": "pr0jectuuid",
"routes": [
{
"from": "monitor",
"name": "monitor-to-viewer",
"to": "viewer"
}
],
"status": "running"
}
Note that an app consists of one or more microservices (containers).
Use edgectl get microservices:
$ edgectl get microservices --app edgeworx-heart-rate
NAME STATUS IMAGE NODE
monitor RUNNING edgeworx/healthcare-heart-rate:arm-v1 west-sf-rnd2346fadc292082f70ed0
viewer RUNNING edgeworx/healthcare-heart-rate-ui-arm:1.0.0 west-sf-rnd2346fadc292082f70ed0
To view the details of the monitor microservice in the edgeworx-heart-rate app:
edgectl get microservice --app edgeworx-heart-rate monitor
Container Logs
You can use the edgectl logs command to view the container logs for a microservice. This is
effectively equivalent to executing docker logs CONTAINER_ID. The logs command takes one
argument, APP_NAME/MICROSERVICE_NAME. For example:
$ edgectl logs edgeworx-heart-rate/monitor --tail 5
[Thu Feb 24 2022 20:52:49] [LOG] test-mode = true, generating mock sensor data..
[Thu Feb 24 2022 20:52:54] [LOG] Retrieving heart rate sensor reading
[Thu Feb 24 2022 20:52:54] [LOG] test-mode = true, generating mock sensor data..
[Thu Feb 24 2022 20:52:59] [LOG] Retrieving heart rate sensor reading
[Thu Feb 24 2022 20:52:59] [LOG] test-mode = true, generating mock sensor data..
Note that you can use the typical logs arguments, such as
--tail 100or--follow.
The following section will go into detail about application YAML files.